Which country has the highest carbon dioxide emissions per capita?
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) is one of the main greenhouse gases, and its excess in the atmosphere is driving climate change. While we often assume larger countries are the biggest polluters, it’s insightful to examine emissions per capita. This analysis takes a closer look at the countries with the highest CO₂ emissions per person, highlighting differences in energy consumption and economic development.
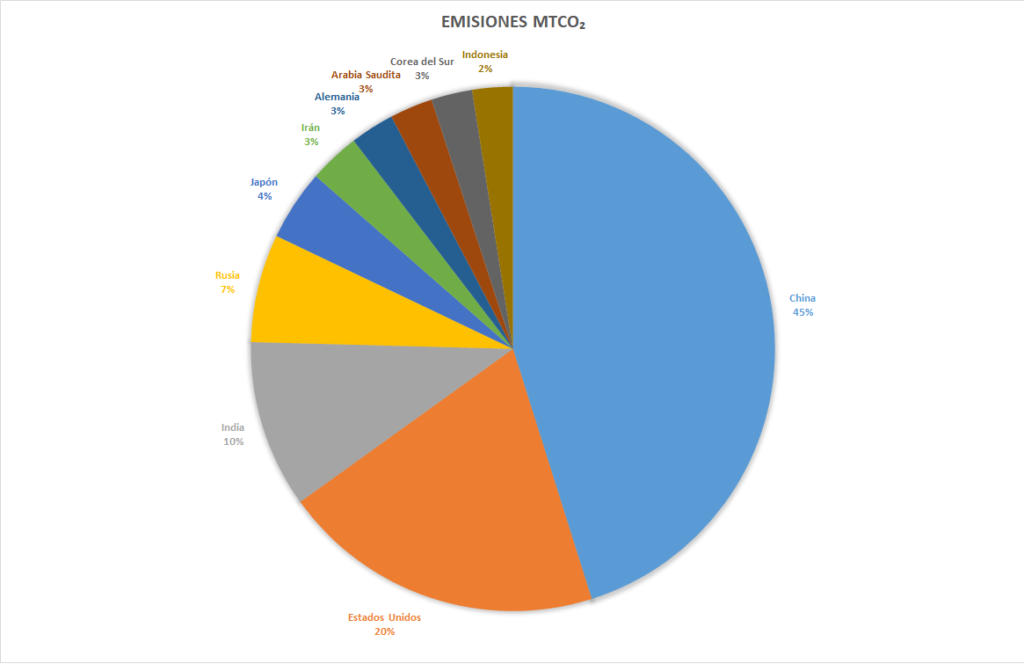
Top Global CO₂ Emitters by Total Volume
In absolute terms, China, the United States, and India account for nearly half of global carbon dioxide emissions. China leads the global ranking with over 10 billion tons of CO₂ emitted annually. However, when we look at CO₂ emissions per person, the list changes dramatically.
Which Country Has the Highest CO₂ Emissions per Capita?
While China emits the highest total volume of CO₂, the small state of Qatar tops the global ranking in per capita emissions. Qatar emits over 40 tons of CO₂ per person annually, driven by its heavy reliance on hydrocarbon extraction and high energy demand. Other countries with high emissions per capita include Kuwait, the United Arab Emirates, and Brunei.
Factors Influencing Per Capita Emissions
Several factors explain why some countries have such high emissions per capita:
- Dependence on fossil fuels: Hydrocarbon-rich nations like Qatar and Kuwait rely heavily on oil and gas extraction, leading to significant CO₂ emissions.
- Low population density: In countries like Australia and Canada, vast distances between cities and relatively low populations mean that transportation and energy use have a high environmental cost per person.
- Heavy industry: Countries like China and Russia, while not leaders in per capita emissions, produce vast amounts of CO₂ due to heavy industries and reliance on coal.
Comparison with Countries with Lower Per Capita Emissions
In contrast, some countries with more sustainable energy models or less reliance on fossil fuels have much lower emissions. Costa Rica, for example, primarily uses renewable energy, resulting in one of the lowest CO₂ emissions per capita. Another example is France, where extensive use of nuclear energy helps keep per capita emissions low compared to other developed nations.
Environmental Consequences of High Per Capita Emissions
Countries with high per capita emissions face significant sustainability challenges. CO₂ emissions contribute to global warming, leading to rising sea levels, more intense storms, and an increased frequency of natural disasters. To meet global climate goals, it is crucial for these countries to adopt stricter policies to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, if you’re wondering what 1 ton of CO₂ represents, you can read more in our dedicated article, where we detail the impact of this amount of emissions and its equivalence in various contexts.
Global Actions to Reduce Per Capita Emissions
International organizations like the United Nations and agreements such as the Paris Agreement are actively working to reduce carbon footprints and lower per capita emissions worldwide. Despite commitments from developed nations, emerging economies often argue that it is unfair to reduce emissions now, considering that developed countries have historically built their prosperity through heavy use of fossil fuels. Striking a balance between economic growth and environmental responsibility remains a significant challenge.
Conclusion: The Challenge of Reducing Per Capita Emissions
Reducing CO₂ emissions per capita is a crucial step in addressing climate change. Countries like Qatar, Kuwait, and Australia, which have high carbon footprints per person, must lead by example by adopting clean energy policies and transitioning away from fossil fuels. Meanwhile, nations like France and Costa Rica show that focusing on renewable energy can significantly reduce carbon emissions without compromising economic growth. Global collaboration is essential to meet climate goals and ensure a more sustainable future for everyone.



