Which country has the highest carbon footprint in the world? The carbon footprint of a country measures the total amount of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, primarily carbon dioxide (CO₂), produced by industrial activities, fossil fuel use, and other human actions affecting the climate. Although CO₂ has a lower global warming potential compared to other GHGs, it is the most abundant and can remain in the atmosphere for over 100 years, worsening climate change.
In today’s landscape, there is a clear disparity in emission contributions between countries. According to recent data, a small group of nations is responsible for the majority of global CO₂ emissions. These countries, with large industries, high dependence on fossil fuels, and large populations, have a significantly higher carbon footprint than the rest of the world.
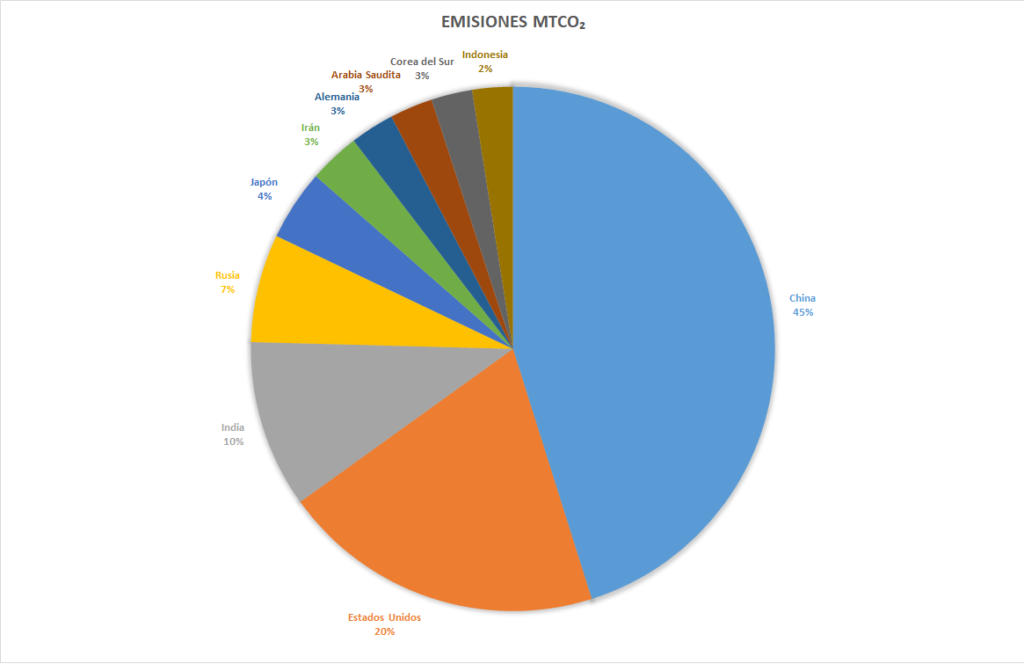
The 10 Countries with the Highest Carbon Footprint
Each year, more than 36 billion tons of CO₂ are emitted into the atmosphere, with only a few countries accounting for nearly 70% of those emissions. Here’s the ranking of the 10 countries with the highest carbon footprint in the world:
- China: 10.668 billion tons of CO₂ emitted.
- United States: 4.713 billion tons of CO₂ emitted.
- India: 2.442 billion tons of CO₂ emitted.
- Russia: 1.577 billion tons of CO₂ emitted.
- Japan: 1.031 billion tons of CO₂ emitted.
- Iran: 745 million tons of CO₂ emitted.
- Germany: 644 million tons of CO₂ emitted.
- Saudi Arabia: 626 million tons of CO₂ emitted.
- South Korea: 598 million tons of CO₂ emitted.
- Indonesia: 590 million tons of CO₂ emitted.
These countries are responsible for a significant percentage of global CO₂ emissions due to their large economies and high consumption of fossil fuels.
China: The Country with the Highest Carbon Footprint
China, the most populous nation in the world, has become the largest emitter of CO₂. Currently, China accounts for about 30% of global emissions. This staggering percentage is primarily due to its heavy reliance on coal to generate electricity and power its vast industrial network.
Despite efforts by the Chinese government to transition toward cleaner energy sources, such as solar and wind power, the country’s dependence on coal remains a key factor in its carbon footprint. In recent years, China has launched major plans to reduce its emissions, aiming to peak emissions by 2030 and become carbon neutral by 2060.
United States: The Second Largest Emitter
The United States ranks second in global emissions, contributing around 14% of global CO₂ emissions. Although its carbon footprint is significantly smaller than China’s, it remains one of the most impactful nations due to its high energy consumption and reliance on fossil fuels for transportation, electricity production, and industry.
In recent years, the country has experienced fluctuations in its emissions. Environmental policies have shifted with each administration, and while the U.S. rejoined the Paris Agreement in 2021 after leaving under the previous administration, its ability to significantly reduce emissions will depend on the implementation of ambitious climate policies.
India: Economic Growth and Rising Emissions
India is the third-largest emitter of CO₂ in the world, with over 2.4 billion tons of CO₂ emitted annually. Although its carbon footprint per capita is much lower than that of China or the United States, the rapid growth of its economy and massive industrialization have led to a significant increase in its emissions.
India relies heavily on coal to meet its energy needs, contributing to its high carbon footprint. However, the country has been proactive in adopting renewable energy and has set an ambitious goal of generating 175 GW of renewable energy by 2022.
Factors Influencing a Country’s Carbon Footprint
A country’s CO₂ emissions depend on several key factors:
- Population: Countries with large populations, like China and India, tend to have bigger carbon footprints due to the high energy demand.
- Fossil fuel use: Nations heavily reliant on coal, oil, and gas for energy production and industry tend to emit more CO₂.
- Industrial development: Countries with large and growing industrial sectors produce higher emissions due to the burning of fossil fuels and manufacturing processes.
- Environmental policies: Regulations and compliance with international agreements, like the Paris Agreement, play a crucial role in CO₂ emissions. Countries with stricter policies on clean energy and sustainable technologies generally have lower carbon footprints.
Which Countries Have the Highest Carbon Footprint Per Capita?
While China, the United States, and India are the largest emitters in absolute terms, the carbon footprint per capita tells a different story. Countries like Qatar, Mongolia, and Kuwait have the highest per capita emissions in the world. This is largely due to their reliance on oil and gas, along with a high standard of living that drives energy consumption.
Carbon Footprint Per Capita Ranking:
- Qatar
- Mongolia
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Brunei
- Kuwait
Which Country Has the Highest Carbon Footprint in the World? The Urgency of Reducing the Global Carbon Footprint
Climate change caused by CO₂ emissions is one of the greatest challenges the world faces today. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), it is crucial to reduce emissions across all sectors if we are to limit global warming to 1.5ºC and avoid irreversible consequences.
Countries like China and the United States have taken steps to reduce their dependence on fossil fuels, but current efforts are not enough to meet the targets set in the Paris Agreement.