What Are the 7 Types of Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy is becoming more essential as the world shifts away from fossil fuels to combat climate change. But what exactly are the main types of renewable energy sources that power our planet? In this article, we’ll explore the seven key types of renewable energy, how they work, and their importance in creating a sustainable future.
1. Solar Energy
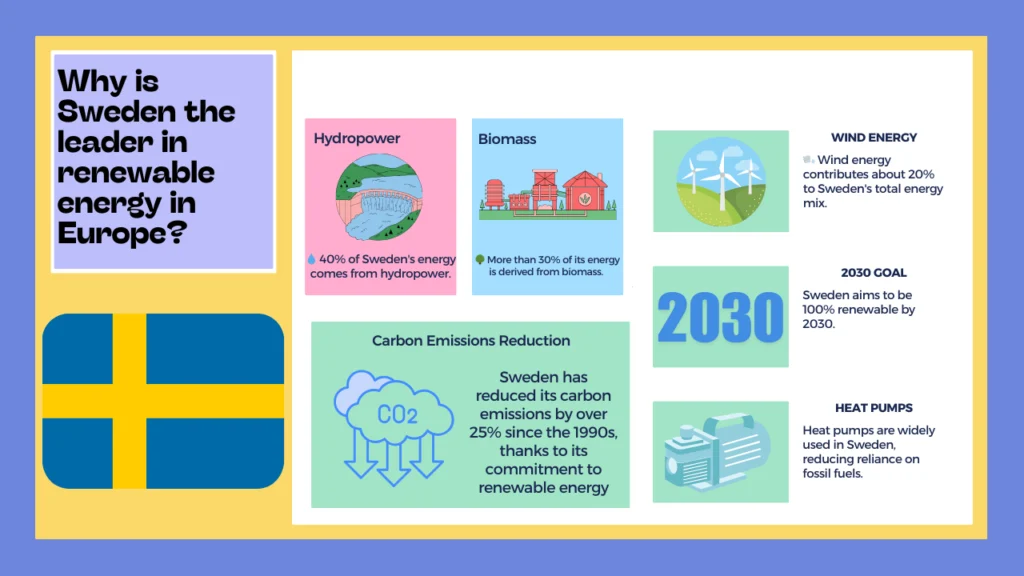
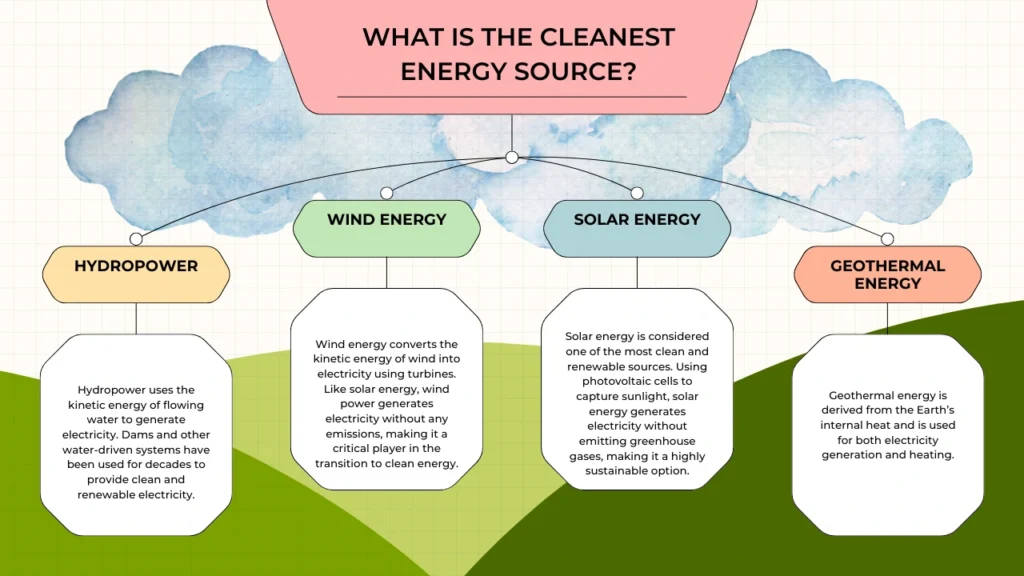
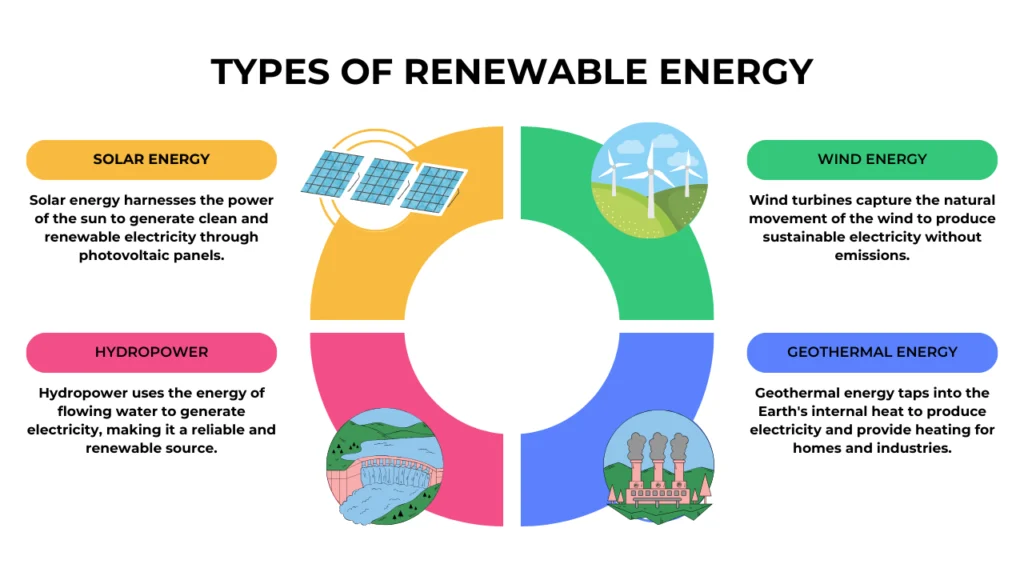
Solar energy is one of the most widely known and used types of renewable energy. It harnesses the power of the sun’s rays using photovoltaic cells to generate electricity. Solar panels are commonly installed on rooftops or large solar farms and convert sunlight into usable power.
- How It Works: Photovoltaic cells absorb sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity, which is then transformed into alternating current (AC) for use in homes and businesses.
- Benefits: Solar energy is abundant, clean, and available almost anywhere in the world.
2. Wind Energy
Wind energy captures the natural movement of the wind through wind turbines to generate electricity. It is especially effective in open areas and offshore locations where wind speeds are higher.
- How It Works: Wind turns the blades of a turbine, which then spins a generator to produce electricity.
- Benefits: Wind energy is renewable, produces no emissions, and is becoming increasingly cost-effective.
3. Hydropower
Hydropower uses the energy of flowing water, typically from rivers or dams, to generate electricity. It is one of the oldest and most reliable forms of renewable energy.
- How It Works: Water flows through turbines in a dam, spinning them to generate electricity.
- Benefits: Hydropower is consistent and can provide large-scale electricity with minimal emissions.
4. Biomass Energy
Biomass energy is derived from organic materials like wood, crop waste, and even household waste. It can be burned to produce heat or converted into biofuels for transportation.
- How It Works: Biomass is burned in power plants to generate heat, which produces electricity. Alternatively, biomass can be transformed into biofuels such as ethanol or biodiesel.
- Benefits: Biomass helps reduce waste and provides a renewable source of energy.
5. Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy taps into the Earth’s internal heat to generate electricity or provide direct heating for buildings. It is most effective in regions with high tectonic activity, such as Iceland or the western United States.
- How It Works: Wells are drilled deep into the Earth to access hot water or steam, which is used to turn turbines and generate electricity.
- Benefits: Geothermal energy is reliable and can produce a constant supply of power, day or night.
6. Tidal Energy
Tidal energy uses the natural rise and fall of ocean tides to produce electricity. Although it’s still in the early stages of development, tidal energy has great potential, especially in coastal regions.
- How It Works: Tidal currents spin underwater turbines, generating electricity in a way similar to wind energy.
- Benefits: Tidal energy is predictable, renewable, and has minimal environmental impact.
7. Ocean Energy (Wave Energy)
Ocean energy or wave energy captures energy from the movement of the ocean’s waves. Like tidal energy, it is a growing field of renewable energy research with high potential.
- How It Works: Specialized devices floating on the surface of the ocean harness wave motion to generate electricity.
- Benefits: Ocean energy is abundant and constant, providing a significant opportunity for coastal areas.
Conclusion: The Future of Renewable Energy
The seven types of renewable energy—solar, wind, hydropower, biomass, geothermal, tidal, and ocean energy—are crucial in the global transition to cleaner energy. Each plays a unique role in reducing our carbon footprint and mitigating the effects of climate change. Learn more about how to calculate and reduce your carbon footprint.