Renewable energy is at the forefront of the global transition towards sustainable living. Among the various types, it is often debated which is the best renewable energy source in terms of efficiency, environmental impact, and long-term sustainability. In this article, we will explore the different types of renewable energy and identify which one stands out as the most efficient and beneficial for our planet.
What Makes a Renewable Energy Source the Best?
To determine the best renewable energy, we must consider various factors, including:
- Efficiency: How effectively can the energy source convert natural resources into usable electricity?
- Environmental impact: Does the energy source minimize harm to ecosystems and reduce carbon emissions?
- Sustainability: Can it provide a long-term, consistent source of energy without depleting resources?
- Economic feasibility: Is it cost-effective, both in terms of setup and ongoing maintenance?
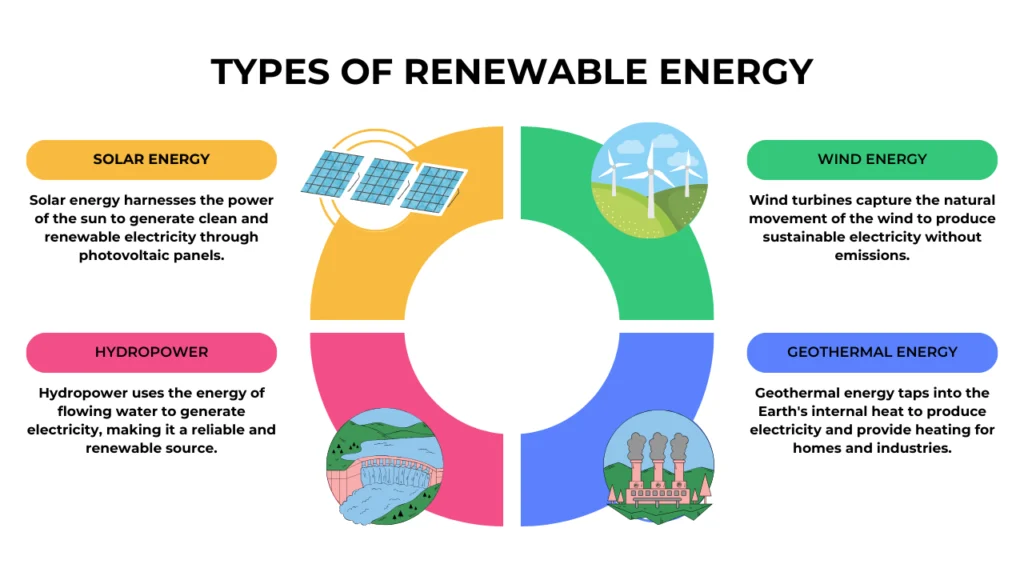
Types of Renewable Energy and Their Benefits
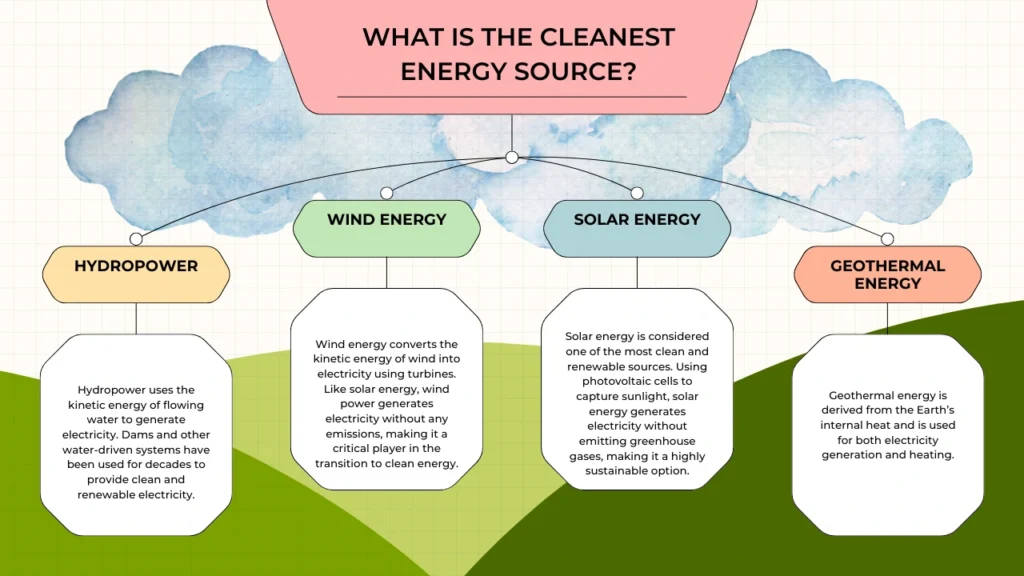
Solar Power
Solar power is one of the most popular forms of renewable energy. It captures energy from the sun using photovoltaic (PV) cells, which convert sunlight directly into electricity. Solar panels can be installed on rooftops, open fields, or even floating on bodies of water.
- Efficiency: The efficiency of solar panels can reach up to 22%, with advancements in solar technology pushing this further. Solar energy is highly efficient in sunny regions, but its performance can drop in cloudy areas or during nighttime.
- Environmental Impact: Solar power produces no emissions during operation. However, the production of solar panels involves the use of materials that require careful disposal at the end of their lifecycle.
- Cost: Initial installation costs can be high, but ongoing operational costs are low, with many countries offering incentives for solar energy adoption.
Wind Power
Wind energy harnesses the power of the wind through turbines, converting kinetic energy into electricity. It’s particularly effective in coastal and open areas where wind speeds are higher.
- Efficiency: Wind turbines have an energy efficiency of about 50-60%, making wind power one of the most efficient renewable sources. Offshore wind farms tend to be even more effective due to stronger and more consistent winds.
- Environmental Impact: Wind power generates zero emissions during operation, though there are concerns about its impact on bird and bat populations. Nevertheless, these impacts are considered minimal compared to fossil fuel emissions.
- Cost: Wind energy is cost-effective, with the cost per kilowatt-hour being among the lowest of all energy sources. Maintenance and land use are relatively minimal once turbines are installed.
Hydropower
Hydropower uses the energy of flowing water to generate electricity, typically through dams or turbines placed in rivers. It has been used for centuries and remains one of the most reliable sources of renewable energy.
- Efficiency: Hydropower is extremely efficient, with energy conversion rates of up to 90%, making it the most efficient large-scale renewable energy source.
- Environmental Impact: Although hydropower is clean in terms of emissions, the construction of dams can significantly alter ecosystems, displacing wildlife and affecting water quality downstream.
- Cost: Hydropower is cost-effective over the long term, but building dams requires significant initial investment and can be geographically limiting.
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy taps into the Earth’s internal heat to generate electricity or provide heating. This energy source is available in areas with volcanic activity, such as Iceland, the Philippines, and parts of the United States.
- Efficiency: Geothermal plants operate at about 45% efficiency. The energy is available year-round, regardless of weather conditions, making it a consistent source of power.
- Environmental Impact: Geothermal energy has a low environmental impact compared to fossil fuels. However, drilling into the Earth’s crust can release trapped gases, and it’s location-specific, limiting its widespread use.
- Cost: High initial costs for drilling and setup, but once operational, the costs are low, with minimal maintenance required.
Biomass Energy
Biomass energy comes from organic materials such as wood, agricultural residues, and even waste. This energy source can be burned directly for heat or converted into biofuels for transportation.
- Efficiency: Biomass energy has a lower efficiency compared to other renewables, generally around 30-50%, depending on the process used.
- Environmental Impact: While it is renewable, biomass can still produce carbon emissions when burned. However, it is considered carbon-neutral because the CO2 released is offset by the CO2 absorbed by the plants during their growth.
- Cost: Biomass can be cost-effective, particularly when using waste materials, but it is less efficient than solar or wind energy.
Tidal Energy
Tidal energy harnesses the power of ocean tides. This technology is still in development but has great potential in coastal regions with significant tidal ranges.
- Efficiency: Tidal power has an efficiency of about 80%, but it is highly dependent on location and tidal patterns.
- Environmental Impact: Tidal energy is clean, but installations can affect marine ecosystems and navigation.
- Cost: Tidal energy infrastructure is expensive, and the technology is still evolving, making it less widely adopted than other renewable sources.
Which Is the Best Renewable Energy?
Based on efficiency, environmental impact, and long-term viability, wind energy stands out as the best renewable energy source. Wind turbines can be installed onshore or offshore, making them highly versatile, and they have one of the highest energy conversion rates. Wind energy also leaves a minimal environmental footprint once the turbines are installed, with low maintenance and operational costs.
Furthermore, wind power is expected to account for 35% of global electricity production within the next 20 years. This positions it as not only the most efficient but also one of the fastest-growing renewable energy sources.
The Future of Renewable Energy
While wind energy is currently the best renewable energy option, the future holds great potential for other technologies. For example, space-based solar farms could capture sunlight outside the Earth’s atmosphere, providing continuous energy without interruptions due to weather or nighttime. Additionally, advancements in quantum dot solar technology and core geothermal energy could revolutionize the energy landscape.
Conclusion
In the race towards a sustainable future, wind energy is the clear leader in terms of efficiency and scalability, helping to significantly reduce our carbon footprint. Use our carbon footprint calculator here to measure how adopting renewable energy can lower your personal emissions. However, Solar, hydropower, and geothermal energy are also vital in reducing our global carbon footprint. Learn more about the relationship between renewable energy and carbon emissions in our article on Climate Change and Carbon Footprint. As technology continues to advance, the renewable energy sector will likely see even more breakthroughs that enhance efficiency and expand access to clean energy worldwide.